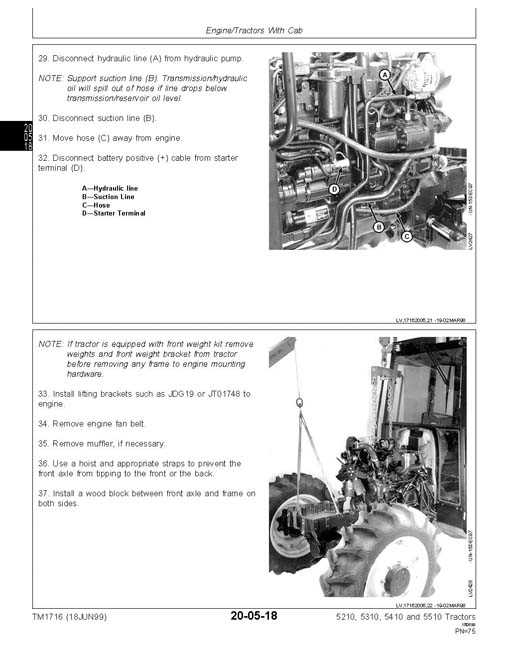
For individuals who possess a specific agricultural vehicle, understanding its features, maintenance, and operational guidelines is crucial for optimal performance. This section aims to provide essential insights into the various aspects of vehicle management, enhancing the user experience and ensuring longevity.
Detailed instructions and practical advice will empower owners to navigate potential challenges and maximize efficiency. From routine upkeep to troubleshooting, this guide offers a wealth of information designed to support users in their journey with their machinery.
By familiarizing oneself with the intricacies of this robust vehicle, operators can ensure smooth functionality and a productive agricultural experience. Whether you are new to the machinery or seeking to refine your skills, the information contained within is an invaluable resource.
Overview of John Deere 5410 Features

This section provides a comprehensive look at the distinctive characteristics and functionalities of a renowned agricultural machine. Designed for efficiency and versatility, this equipment stands out in the field for its reliability and performance.
- Powerful Engine: Equipped with a robust powertrain, ensuring optimal performance for various tasks.
- Advanced Hydraulics: Features a hydraulic system that enhances lifting capabilities and improves maneuverability.
- Ergonomic Design: Built with user comfort in mind, allowing for easier operation during extended periods.
- Versatile Attachments: Compatible with a range of implements, making it suitable for different agricultural applications.
- Durability: Constructed with high-quality materials to withstand tough working conditions.
These features collectively enhance productivity, making this model a preferred choice among agricultural professionals.
Maintenance Guidelines for Optimal Performance
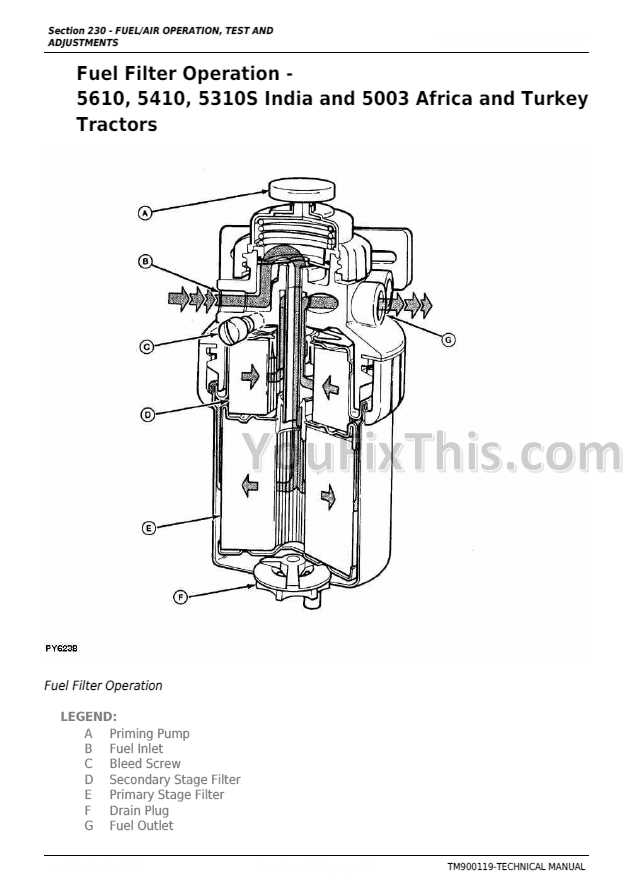
Ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your machinery requires a proactive approach to upkeep. Regular maintenance not only enhances performance but also minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns. Implementing a structured routine can lead to significant improvements in functionality and reliability.
The following table outlines essential maintenance tasks and their recommended frequencies:
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Oil Change | Every 100 hours of operation |
| Filter Replacement | Every 200 hours of operation |
| Tire Inspection | Monthly |
| Belt Check | Every 50 hours of operation |
| Battery Maintenance | Every 6 months |
Following these guidelines will ensure that your equipment operates at its best and reduces the likelihood of costly repairs. Regular checks and timely interventions can extend the lifespan of your machinery significantly.
Troubleshooting Common Operational Issues

When operating heavy machinery, various challenges may arise that can hinder performance. Identifying and addressing these problems promptly is essential to maintain efficiency and safety. This section provides insights into common issues encountered during operation and practical solutions to resolve them.
One frequent complication is the engine failing to start. This can stem from multiple factors, such as a depleted battery or fuel supply issues. To resolve this, check the battery connections and ensure there is sufficient fuel in the tank.
Another common concern involves unusual noises while operating the equipment. These sounds can indicate mechanical wear or loose components. Inspecting the belts and bearings can help pinpoint the source of the noise and facilitate necessary repairs.
Overheating is also a typical issue that operators may face. This can result from insufficient coolant levels or a malfunctioning radiator. Regularly checking coolant levels and ensuring proper airflow around the engine can prevent overheating problems.
Finally, poor performance during operation can be linked to filter clogs or improper settings. Regular maintenance of air and fuel filters, along with calibrating settings to match operational requirements, can significantly enhance overall functionality.