
Understanding the intricacies of agricultural machinery is essential for maximizing productivity on the farm. This section delves into the essential aspects of operating and maintaining a specific type of forage harvesting equipment, ensuring optimal performance throughout its lifespan.
Proper guidance allows users to navigate the functionalities and features effectively, ensuring that tasks such as baling are performed with precision. It is crucial to familiarize oneself with the operating techniques, maintenance schedules, and troubleshooting tips to enhance both efficiency and longevity.
Additionally, insights into best practices for regular upkeep and safety protocols will empower operators to make informed decisions. Mastering these elements not only improves overall yield but also contributes to a safer working environment.

This section will delve into the essential characteristics and functionalities of the equipment designed for efficient agricultural practices. Understanding these elements is crucial for maximizing productivity and ensuring seamless operation.
- Design and Structure
- Operational Mechanisms
- Maintenance Requirements
- Safety Features
- Performance Metrics
Each feature plays a vital role in the overall efficiency and effectiveness of the machinery. Familiarizing oneself with these aspects not only enhances usability but also contributes to better maintenance and longevity of the equipment.
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular upkeep is essential for ensuring that your equipment operates smoothly and efficiently. Implementing a consistent maintenance routine not only enhances performance but also extends the lifespan of the machinery. Below are some fundamental practices to consider.
Routine Inspections
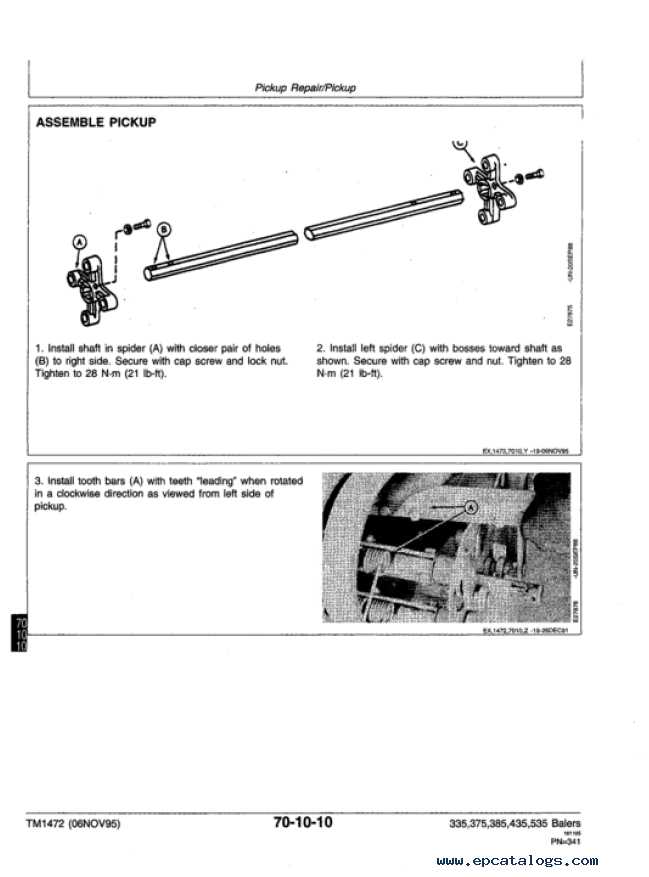
Conducting frequent inspections is crucial for identifying potential issues before they escalate. Check key components such as belts, gears, and hydraulic systems to ensure they are functioning correctly. Early detection of wear and tear can save time and repair costs.
Lubrication Schedule

Proper lubrication of moving parts reduces friction and prevents premature wear. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricant types and application frequency. Keeping components well-lubricated ensures smoother operation and enhances overall efficiency.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Inspect belts and gears | Every 50 hours |
| Change oil and filters | Every 100 hours |
| Lubricate moving parts | Every 25 hours |
Common Issues and Troubleshooting Guide

This section aims to address frequent challenges that operators may encounter with their equipment. Understanding these issues can help in maintaining optimal performance and ensuring longevity.
1. Difficulty Starting: If the machinery does not start, check the fuel supply and battery connections. Ensure that all safety mechanisms are properly engaged.
2. Unusual Noises: Listen for any abnormal sounds during operation. These could indicate mechanical wear or insufficient lubrication. Regular inspections can prevent major breakdowns.
3. Poor Performance: If the efficiency drops, examine the settings and ensure they match the current task requirements. Clogged filters or dull blades can also contribute to reduced output.
4. Overheating: Excessive heat can lead to serious damage. Monitor the temperature and check coolant levels. Ensure that airflow is not obstructed.
5. Frequent Jamming: If the unit frequently jams, inspect for blockages and ensure that materials are fed correctly. Adjusting feed rates may also alleviate this issue.
6. Electrical Failures: Inspect wiring and connections if electrical problems arise. Corrosion or loose connections can disrupt functionality. Regular maintenance of electrical components is crucial.
By addressing these common challenges proactively, users can enhance the reliability and efficiency of their machinery.